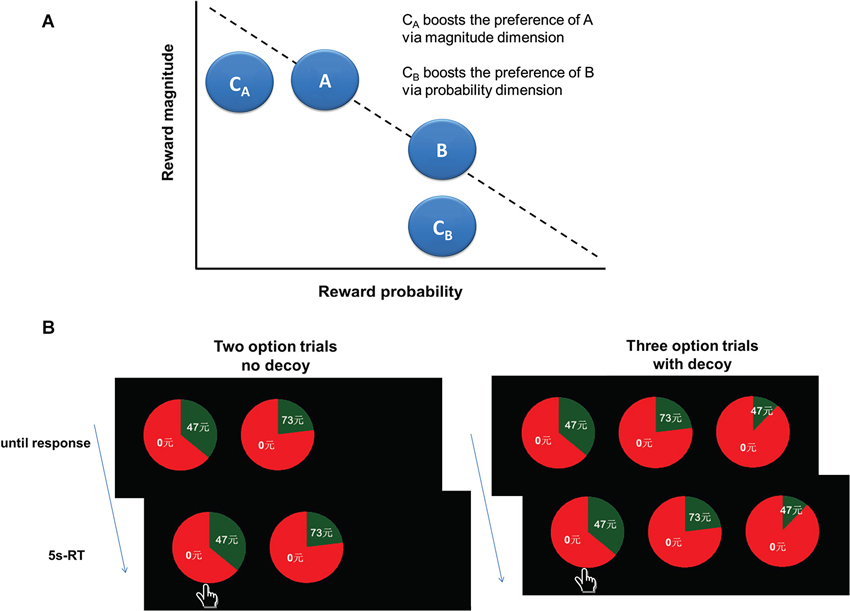
Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics . the decoy effect is an example of a behavioral nudge—a type of intervention that “steers” individuals towards making a certain choice. Nudges do not manipulate behavior by providing large incentives to behave a certain way or threatening some form of punishment for failing to do so. discover how the decoy effect, a phenomenon that influences our choices by adding a third option, works and why it. the decoy effect is a phenomenon in which people’s preferences between two options change depending on the presence of a. the decoy effect or the asymmetric dominance effect is a cognitive bias in which consumers will tend to have a specific change in. the decoy effect may well be one of the most famous of human biases (frederick et al., 2014) that violates neoclassical economics’. we discuss and differentiate four types of decoy alternatives that produce three types of decoy effects:
from www.frontiersin.org
the decoy effect or the asymmetric dominance effect is a cognitive bias in which consumers will tend to have a specific change in. the decoy effect is a phenomenon in which people’s preferences between two options change depending on the presence of a. Nudges do not manipulate behavior by providing large incentives to behave a certain way or threatening some form of punishment for failing to do so. we discuss and differentiate four types of decoy alternatives that produce three types of decoy effects: discover how the decoy effect, a phenomenon that influences our choices by adding a third option, works and why it. the decoy effect may well be one of the most famous of human biases (frederick et al., 2014) that violates neoclassical economics’. the decoy effect is an example of a behavioral nudge—a type of intervention that “steers” individuals towards making a certain choice.
Frontiers The neural correlates of the decoy effect in decisions Behavioral Neuroscience
Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics the decoy effect or the asymmetric dominance effect is a cognitive bias in which consumers will tend to have a specific change in. the decoy effect is an example of a behavioral nudge—a type of intervention that “steers” individuals towards making a certain choice. discover how the decoy effect, a phenomenon that influences our choices by adding a third option, works and why it. we discuss and differentiate four types of decoy alternatives that produce three types of decoy effects: the decoy effect is a phenomenon in which people’s preferences between two options change depending on the presence of a. the decoy effect or the asymmetric dominance effect is a cognitive bias in which consumers will tend to have a specific change in. Nudges do not manipulate behavior by providing large incentives to behave a certain way or threatening some form of punishment for failing to do so. the decoy effect may well be one of the most famous of human biases (frederick et al., 2014) that violates neoclassical economics’.
From www.simplimba.com
The Decoy Effect Revealing 7 Facts behind the Invisible Force Of Your Choices SimpliMBA Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics discover how the decoy effect, a phenomenon that influences our choices by adding a third option, works and why it. we discuss and differentiate four types of decoy alternatives that produce three types of decoy effects: the decoy effect or the asymmetric dominance effect is a cognitive bias in which consumers will tend to have a specific. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From firstlinesecurities.com
The Decoy Effect & How It Affects Your Finances Firstline Securities Limited Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics discover how the decoy effect, a phenomenon that influences our choices by adding a third option, works and why it. the decoy effect is a phenomenon in which people’s preferences between two options change depending on the presence of a. we discuss and differentiate four types of decoy alternatives that produce three types of decoy effects: . Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From cr8consultancy.com
The Decoy Effect Marketing Psychology Tricks That Make You Spend More CR8 Consultancy Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics we discuss and differentiate four types of decoy alternatives that produce three types of decoy effects: the decoy effect or the asymmetric dominance effect is a cognitive bias in which consumers will tend to have a specific change in. the decoy effect is an example of a behavioral nudge—a type of intervention that “steers” individuals towards making. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From 602communications.com
Decoy Effect Graeme Newell Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics discover how the decoy effect, a phenomenon that influences our choices by adding a third option, works and why it. Nudges do not manipulate behavior by providing large incentives to behave a certain way or threatening some form of punishment for failing to do so. the decoy effect or the asymmetric dominance effect is a cognitive bias in. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From www.youtube.com
The Decoy Effect Theory & Examples YouTube Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics the decoy effect may well be one of the most famous of human biases (frederick et al., 2014) that violates neoclassical economics’. we discuss and differentiate four types of decoy alternatives that produce three types of decoy effects: discover how the decoy effect, a phenomenon that influences our choices by adding a third option, works and why. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From bizzbucket.co
Decoy effect Why it matters in business? BizzBucket Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics the decoy effect may well be one of the most famous of human biases (frederick et al., 2014) that violates neoclassical economics’. the decoy effect is a phenomenon in which people’s preferences between two options change depending on the presence of a. the decoy effect or the asymmetric dominance effect is a cognitive bias in which consumers. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From www.deconstructoroffun.com
with Behavioral Economics — Deconstructor of Fun Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics the decoy effect is a phenomenon in which people’s preferences between two options change depending on the presence of a. the decoy effect may well be one of the most famous of human biases (frederick et al., 2014) that violates neoclassical economics’. the decoy effect or the asymmetric dominance effect is a cognitive bias in which consumers. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) The neural correlates of the decoy effect in decisions Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics discover how the decoy effect, a phenomenon that influences our choices by adding a third option, works and why it. Nudges do not manipulate behavior by providing large incentives to behave a certain way or threatening some form of punishment for failing to do so. the decoy effect may well be one of the most famous of human. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From 602communications.com
What is the Decoy Effect Cognitive Bias? Graeme Newell Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics the decoy effect or the asymmetric dominance effect is a cognitive bias in which consumers will tend to have a specific change in. the decoy effect is a phenomenon in which people’s preferences between two options change depending on the presence of a. discover how the decoy effect, a phenomenon that influences our choices by adding a. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From www.simplimba.com
The Decoy Effect Revealing 7 Facts behind the Invisible Force Of Your Choices SimpliMBA Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics we discuss and differentiate four types of decoy alternatives that produce three types of decoy effects: the decoy effect or the asymmetric dominance effect is a cognitive bias in which consumers will tend to have a specific change in. Nudges do not manipulate behavior by providing large incentives to behave a certain way or threatening some form of. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From exoolainz.blob.core.windows.net
Decoy Effect Economics at Royce Fields blog Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics the decoy effect is an example of a behavioral nudge—a type of intervention that “steers” individuals towards making a certain choice. the decoy effect may well be one of the most famous of human biases (frederick et al., 2014) that violates neoclassical economics’. the decoy effect or the asymmetric dominance effect is a cognitive bias in which. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From cleverads.com.ph
What is the Decoy effect? How it stimulates customer Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics we discuss and differentiate four types of decoy alternatives that produce three types of decoy effects: the decoy effect is a phenomenon in which people’s preferences between two options change depending on the presence of a. the decoy effect is an example of a behavioral nudge—a type of intervention that “steers” individuals towards making a certain choice.. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From www.youtube.com
decoy effect behavioural economics YouTube Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics we discuss and differentiate four types of decoy alternatives that produce three types of decoy effects: Nudges do not manipulate behavior by providing large incentives to behave a certain way or threatening some form of punishment for failing to do so. the decoy effect or the asymmetric dominance effect is a cognitive bias in which consumers will tend. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From medium.com
Unraveling the Decoy Effect The Psychology of Buying Behavior by Kasim Aslam Feb, 2024 Medium Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics the decoy effect or the asymmetric dominance effect is a cognitive bias in which consumers will tend to have a specific change in. discover how the decoy effect, a phenomenon that influences our choices by adding a third option, works and why it. Nudges do not manipulate behavior by providing large incentives to behave a certain way or. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From lifedesignanalysis.com
The Decoy Effect or Asymmetric Dominance Life Design Analysis Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics the decoy effect is a phenomenon in which people’s preferences between two options change depending on the presence of a. the decoy effect or the asymmetric dominance effect is a cognitive bias in which consumers will tend to have a specific change in. the decoy effect may well be one of the most famous of human biases. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From builtformars.com
UX Psychology 🦜 The Decoy Effect Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics the decoy effect is a phenomenon in which people’s preferences between two options change depending on the presence of a. the decoy effect is an example of a behavioral nudge—a type of intervention that “steers” individuals towards making a certain choice. Nudges do not manipulate behavior by providing large incentives to behave a certain way or threatening some. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) DecisionMaking Mechanism in Behavioral Economics The Decoy Effect Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics the decoy effect is a phenomenon in which people’s preferences between two options change depending on the presence of a. we discuss and differentiate four types of decoy alternatives that produce three types of decoy effects: the decoy effect is an example of a behavioral nudge—a type of intervention that “steers” individuals towards making a certain choice.. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.
From mind.help
Behavioral Economics Top 5 Ways It Can Affect Mental Health Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics the decoy effect is an example of a behavioral nudge—a type of intervention that “steers” individuals towards making a certain choice. the decoy effect is a phenomenon in which people’s preferences between two options change depending on the presence of a. we discuss and differentiate four types of decoy alternatives that produce three types of decoy effects:. Decoy Effect Behavioral Economics.